Introduction
Brief Overview of the Article
Welcome to our in-depth exploration of Fibonacci retracement levels, a crucial component of the technical analysis toolkit used by traders worldwide. This article aims to demystify the concept and provide you with a practical understanding of how to use Fibonacci retracement levels effectively in your trading strategy. We will start with the origins of Fibonacci sequences, dive deep into the specific retracement levels, illustrate how to use them in Forex trading, and highlight common mistakes to avoid. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you will be able to leverage the power of Fibonacci retracement levels to make more informed trading decisions.
Explanation of Fibonacci Retracement and its Importance in Trading
Fibonacci retracement is a predictive technical indicator used to estimate possible price retracements, or "pullbacks," within the context of trading. These retracement levels are derived from the Fibonacci sequence, a string of numbers where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones. Starting from zero and one, the sequence goes 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, and so forth.
The significance of Fibonacci retracement in trading lies in its ability to predict potential support and resistance levels. Support and resistance are two key concepts in trading; they refer to price levels where the price tends not to pass through (resistance) or fall below (support). By identifying these levels, traders can make strategic decisions on when to enter or exit a trade, thus optimizing their potential for profit and reducing their risk.
In essence, Fibonacci retracement is not only a tool for prediction but also a vital part of risk management in trading. Understanding and effectively utilizing this tool can drastically enhance your trading acumen and success.
The History of Fibonacci Sequences
The origin of the Fibonacci number sequence
The Fibonacci number sequence finds its roots in the work of an Italian mathematician known as Leonardo of Pisa, more famously recognized as Fibonacci. The sequence made its first appearance in his book "Liber Abaci," published in 1202. In this book, Fibonacci introduced the sequence to the Western world, but it's essential to note that it had already been described in Indian mathematics.
The introduction came in the form of a problem revolving around the growth of a hypothetical population of rabbits. Fibonacci posed that if a pair of mature rabbits (a male and a female) is placed in an enclosed space, and if every month each pair produces another pair, which becomes productive when they are one month old, how many pairs of rabbits will there be at the end of a certain number of months? The solution to this problem led to the formation of the Fibonacci sequence, where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones.
However, the widespread adoption and recognition of the Fibonacci number sequence in the West, especially in technical analysis in trading, can be attributed to Fibonacci's work.

The Mathematical Properties of the Fibonacci Sequence
The Fibonacci sequence is characterized by its unique mathematical properties that contribute to its pervasive presence across diverse fields, from the natural sciences to finance. Here are some of the key mathematical properties:
- The Recurrence Relation: The Fibonacci sequence is defined by the following recurrence relation:
F(n) = F(n-1) + F(n-2)
where F(n) is the nth term in the sequence. The sequence typically starts with F(0) = 0 and F(1) = 1. Using this formula, the following terms can be generated. For example, F(2) would be 1 (since F(2-1) + F(2-2) equals 1 + 0), F(3) would be 2, and so forth.
- The Golden Ratio: As the Fibonacci sequence progresses, the ratio of two consecutive numbers tends towards the Golden Ratio (approximately 1.61803), which is an irrational number. The Golden Ratio, often denoted by the Greek letter phi (Φ), is one of the most surprising and well-known properties of the Fibonacci sequence. For large n, F(n+1)/F(n) is approximately equal to the Golden Ratio.
- Sum of Fibonacci Numbers: Another interesting property is that the sum of any ten consecutive Fibonacci numbers is divisible by 11.
- Square Properties: The square of a Fibonacci number can be expressed as the product of the two surrounding Fibonacci numbers plus or minus one. For example, (F(n))^2 = F(n-1) * F(n+1) + (-1)^n.
These mathematical properties and more make the Fibonacci sequence a fascinating topic of study in various fields, including mathematics, natural science, art, and financial market analysis.
The Application of Fibonacci Sequences in Different Fields
The Fibonacci sequence, thanks to its unique mathematical properties, has been applied in a myriad of fields far beyond the realm of pure mathematics. Here are some key areas where the Fibonacci sequence plays a significant role:
1. Nature and Biology: The Fibonacci sequence appears frequently in the natural world. For instance, the arrangement of leaves on a stem, often called phyllotaxis, often follows a Fibonacci sequence, allowing for the optimal absorption of sunlight. Similarly, the count of petals in many flower species often turns up Fibonacci numbers. The spiral pattern of seeds in a sunflower, the growth of a pine cone, and the spiral of the Nautilus shell - all these are expressions of the Fibonacci sequence in nature.
2. Art and Architecture: The Golden Ratio derived from the Fibonacci sequence has been widely used in arts and architecture, believed to produce aesthetically pleasing proportions. Examples include the Parthenon in Greece, the Pyramids of Egypt, and various works of art throughout history. It's also used in modern design and photography for creating well-balanced and appealing compositions.
3. Computer Science: Fibonacci numbers are used in data structures called Fibonacci heaps. They're also used in algorithms, especially for recursive problems involving data sets that naturally adhere to the Fibonacci sequence (like efficient generation of Fibonacci numbers themselves or certain sorting algorithms).
4. Finance: In finance and particularly in technical analysis of markets, the Fibonacci retracement uses horizontal lines to indicate areas of support or resistance at the key Fibonacci levels before the price continues in the original direction. These levels are calculated by tracing the Fibonacci sequence to identify potential turning points for market prices.
5. Music: Even in music, Fibonacci numbers find application. For instance, the structure of a piano octave, a scale with thirteen keys in which eight of them are white and five are black (split into groups of three and two), aligns with numbers from the Fibonacci sequence.
In these fields and more, the Fibonacci sequence has proven to be an invaluable tool due to its unique mathematical properties and their physical and conceptual manifestations.
Understanding the Concept of Fibonacci Retracement in Trading
Definition of Fibonacci Retracement in the Context of Trading
Fibonacci retracement is a key tool used in technical analysis, providing traders with potential points of strategic actions based on the identification of support and resistance levels. Named after the Fibonacci sequence, it leverages ratios derived from this sequence to predict a portion of the primary trend's movement in which a pullback might end and the trend resumes.
In practical terms, Fibonacci retracement levels are a series of horizontal lines that are used to highlight where possible support and resistance levels are likely to occur. They are calculated by identifying the peak and trough (high and low points) over a specific period on the chart, then dividing the vertical distance between these two points by key Fibonacci ratios: 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 100%.
Each percentage is considered a Fibonacci retracement level where the price could experience a significant increase in buying or selling activity. Traders use these levels to identify strategic positions for transactions, such as entry or exit points, set target prices, and place stop losses. The Fibonacci retracement tool, therefore, serves as a predictive technical indicator aimed at helping traders capitalize on the market fluctuations.

How Fibonacci Retracement Works in the Foreign Exchange Market
In the foreign exchange market, Fibonacci retracement serves as a valuable tool for traders aiming to predict the extent of a currency pair's price correction. These retracement levels provide potential areas of reversal as the price retraces a portion of its previous movement. Here's how it works:
1. Identify Highs and Lows: The first step is to identify significant highs (peak) and lows (trough) on the price chart. This could be over any time frame - intraday, daily, weekly, or even monthly. The peak and trough form the baseline for your Fibonacci retracement.
2. Draw the Levels: Once the highs and lows are identified, you draw six horizontal lines intersecting the trend at the following levels: 0.0%, 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 100%. This is usually done with the help of a Fibonacci tool available in most trading platforms.
3. Interpret the Levels: These lines represent potential reversal zones where price could potentially stall or reverse. The common interpretation is that the price is likely to bounce off these levels and continue in the direction of the primary trend. However, if the price breaks through these levels, it could signal a longer-term retracement or even a reversal of the primary trend.
4. Plan the Trade: Traders use these levels to make trading decisions. For instance, if the trend is bullish, traders might consider opening a long position at a retracement level in anticipation of a bounce. Similarly, in a bearish trend, traders might consider a short position.
Fibonacci retracement in the foreign exchange market allows traders to anticipate potential points of reversal. It's important to remember that Fibonacci retracement is a predictive tool and not a guarantee. It's most effective when used in conjunction with other forms of technical analysis to confirm signals.
The importance of Fibonacci retracement levels in technical analysis
Fibonacci retracement levels play an integral role in technical analysis due to several reasons:
1. Price Prediction: Fibonacci retracement levels provide traders with a way to predict potential future levels of support and resistance. By identifying these key levels, traders can anticipate possible points where price is likely to bounce or reverse, providing guidance for entry and exit points.
2. Risk Management: Knowing where the Fibonacci levels are can help traders manage risk more effectively. Traders can use these levels to set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses if the trade goes against their prediction. Similarly, they can set profit targets at or near Fibonacci levels to maximize profits.
3. Market Psychology: Fibonacci levels often work because traders globally watch and make decisions based on these levels, making them self-fulfilling. The more traders observe and respect these levels, the more significant these levels become.
4. Compatibility with Other Tools: Fibonacci retracement levels work well in conjunction with other technical analysis tools. For example, if a Fibonacci level coincides with a trendline or a key level from a moving average, this level will likely be a stronger support or resistance level. Combining these tools can help improve the accuracy of the analysis and reduce the likelihood of false signals.
5. Versatility: Fibonacci retracements can be used in any market (stocks, commodities, Forex, cryptocurrencies) and on any timeframe, be it short-term trading charts or long-term investment charts.
Therefore, Fibonacci retracement levels are considered an important tool in a trader's arsenal. They help in making more informed trading decisions, manage risk, and understand market trends better. However, it's crucial to remember that like any technical analysis tool, Fibonacci retracements don't guarantee success and should be used alongside other indicators and analysis techniques.
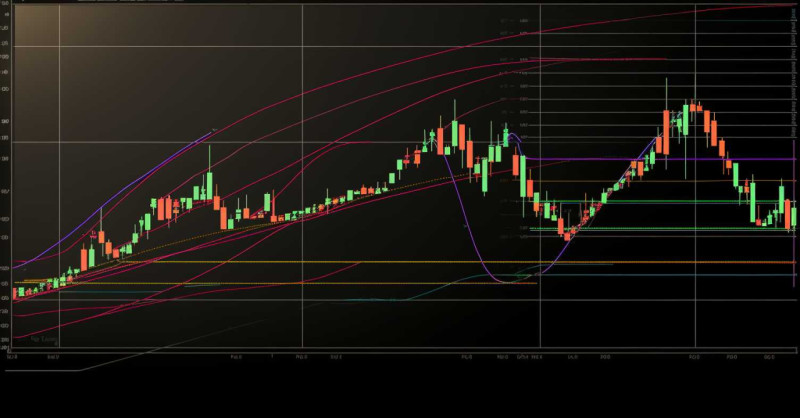
The Fibonacci Retracement Levels
A deep dive into Fibonacci retracement levels: 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 100%
In the context of trading, the Fibonacci retracement levels: 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 100% signify potential zones where prices may find support or resistance. They are derived from the Fibonacci sequence, a series of numbers where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, often starting with 0 and 1.
1. 23.6% Fibonacci Retracement Level:
The 23.6% level is the first retracement level that comes after a significant price movement. This is considered a minor retracement level and often suggests a strong trend where the price is likely to continue in the original direction rather than reverse. However, if the price fails to hold this level, it may move towards the next Fibonacci retracement level.
2. 38.2% Fibonacci Retracement Level:
The 38.2% level is derived by dividing any number in the Fibonacci sequence by the number two places to its right. This level is important in trading as it is the first major retracement level. When a price retraces to this level and then resumes the prior trend, it signifies a fairly strong trend.
3. 50% Fibonacci Retracement Level:
Although the 50% retracement level is not based on a Fibonacci number, it is widely viewed in trading and often serves as a level of reversal or continuation of the trend. It's also considered a psychological level where traders decide to enter or exit trades.
4. 61.8% Fibonacci Retracement Level:
This is the most significant Fibonacci retracement level and is derived by dividing a number in the Fibonacci sequence by the number immediately following it. It's also referred to as the 'golden ratio'. If the price retraces to this level before resuming the previous trend, the trend is considered to be less robust.
5. 100% Fibonacci Retracement Level:
The 100% retracement level signifies that the price has returned to the start of the initial move. In many cases, this could mean a complete reversal in trend.
These levels, drawn between the high and low points of a price chart, provide traders with potential points of market interest where trading activity may spike or price direction may shift. Understanding them is an essential part of implementing Fibonacci retracement into a trading strategy.
Explanation of why these specific levels are significant in trading
The Fibonacci retracement levels derived from the unique mathematical relationships within the Fibonacci sequence are recognized for their predictive capabilities in financial trading. The key Fibonacci levels - 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 100% - have gained significance in trading due to the following reasons:
1. Psychological Markers:
These levels often act as psychological markers for traders, resulting in increased buying or selling pressure at these points. For example, traders might see a retracement to the 61.8% level as an attractive point to enter a trade in the direction of the underlying trend.
2. Areas of Interest:
Fibonacci retracement levels are areas where a lot of trading activity can occur, leading to significant price changes. These levels can act as support or resistance - points where price action tends to pause or change direction.
3. Self-fulfilling Prophecy:
Since a large number of traders worldwide use and respond to these Fibonacci levels, they can often become a self-fulfilling prophecy. The more traders buy at a particular retracement level, the stronger the support at that level becomes, and vice versa for selling and resistance levels.
4. Risk Management:
Fibonacci levels can be used for setting stop-loss and take-profit orders. If a trader identifies a retracement level as potential support, they might set a stop-loss order just below this level.
5. Validation of Trends:
In a strong uptrend or downtrend, retracements tend to terminate at the key Fibonacci levels before the price resumes its original trend. This can help validate the strength of the trend and provide confirmation for traders to enter or stay in trades.
6. Pairing with Other Technical Tools:
Fibonacci retracement levels can provide value when used in conjunction with other technical analysis tools, such as moving averages, trend lines, and other pattern recognition tools. This can create confluence, which strengthens the significance of these levels.
In summary, the specific Fibonacci retracement levels are significant in trading because they offer potential strategic entry and exit points. However, like all technical indicators, they should be used as part of a comprehensive trading strategy and not in isolation.
Graphical illustrations and examples of Fibonacci retracement levels
Let's say you're examining the price movement of a particular stock over a certain period. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Identify Significant Price Points: First, you need to identify a significant price high and a significant price low on the chart. For an upward trend, the low point will be where you start drawing the Fibonacci retracement levels, and the high point is where you stop. For a downward trend, you do the opposite.
Draw the Fibonacci Levels: Using the Fibonacci tool in your charting software, click and drag from the low to the high point (in an uptrend) or from the high to the low point (in a downtrend). The software should automatically plot the key Fibonacci levels (23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 100%) between these two points.
Interpret the Fibonacci Levels: Each line represents a potential support or resistance level where the price could potentially reverse or experience some resistance. Observe how the price behaves at these levels.
For example, let's say you are looking at an upward trend, and the price starts to retrace (go down). If it stops near the 38.2% level and then starts to move up again, that could indicate that this is a level of support. If the price goes through this level, then the next potential support could be at the 50% or 61.8% level.
Please remember that while the Fibonacci retracement tool can be helpful, it should not be used in isolation. Traders usually combine it with other forms of technical analysis to confirm their findings and make more informed decisions.
How to Use Fibonacci Retracement Levels in Trading
Step-by-step Guide on How to Draw Fibonacci Retracement Levels in Trading Platforms
Select the Fibonacci Tool: Most trading platforms have a built-in Fibonacci retracement tool. You'll typically find it in the toolbar or under a menu labeled something like "drawing tools" or "technical analysis tools".
Identify Significant Price Points: You'll need to find a significant high and low on the price chart. For an uptrend, you start at the bottom and draw up to the top. For a downtrend, start at the top and draw down to the bottom.
Draw the Fibonacci Levels: Click on the low point, hold, and drag the cursor to the high point, then release. The platform should automatically draw horizontal lines at the key Fibonacci levels: 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 100%.
Analyze: Examine these levels and how the price interacts with them to help identify potential future areas of support or resistance.
How to Use Fibonacci Retracement Levels for Entry and Exit Points in Trading
Identify Potential Entry Points: When a price retraces to a Fibonacci level and shows signs of resuming the original trend (for instance, through the formation of a bullish candlestick pattern in an uptrend), this could be a potential entry point.
Set Potential Exit or Take-Profit Points: Fibonacci retracement levels can also help determine when to exit a trade. For example, if you're in a long position and the price is approaching a key Fibonacci level, you might consider closing the position or taking profits, expecting the price to retrace.
Consideration of Other Factors: The effectiveness of Fibonacci retracement levels increases when used with other indicators or techniques. Always consider the overall market trends, volume, and other technical analysis tools before making trading decisions.
The Role of Fibonacci Retracement Levels in Risk Management
Setting Stop-Loss Orders: You can place stop-loss orders just beyond a Fibonacci level that you're hoping will serve as support or resistance. For example, if you're expecting the price to bounce off the 61.8% level, you might place a stop-loss order just below this level to limit potential losses if the price breaks through.
Risk-Reward Ratio: Fibonacci retracement levels can help determine a favorable risk-reward ratio. If the distance between your entry point and the next Fibonacci level is greater than the distance between your entry point and your stop-loss level, the trade could be considered favorable.
Avoid Overexposure: As with all trading tools, it's crucial not to rely solely on Fibonacci retracement levels for decision-making. Overexposure can lead to increased risk. Consider other technical indicators and market news to make well-rounded trading decisions.

Advanced Techniques of Fibonacci Retracement
Fibonacci Extensions: Predicting Potential Price Targets
Definition and Calculation: Fibonacci extensions are used by traders to determine potential areas where the price could reach after a retracement is complete. They're calculated by subtracting the end point of the retracement from the start point and then extending this distance from the end point of the retracement.
Common Fibonacci Extension Levels: The most common Fibonacci extension levels are 61.8%, 100%, 161.8%, 200%, and 261.8%. Traders might use these levels to set profit targets or identify where a price movement might find support or resistance.
Practical Application: Discuss how traders use Fibonacci extensions in conjunction with retracement levels for better accuracy in predicting potential price targets.
Fibonacci Fan and Fibonacci Arc: Additional Tools for Trend Analysis
Fibonacci Fan: The Fibonacci fan is a technical tool that uses three diagonal lines based on Fibonacci numbers to predict future levels of support and resistance. These lines are drawn from a trend's high and low points and intersect the Fibonacci retracement levels of 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8%.
Fibonacci Arc: Fibonacci arcs are created by drawing an invisible trendline between two points (usually a high and a low), and then drawing three curves that intersect this line at the Fibonacci levels of 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8%. These arcs can help identify areas of support and resistance.
Comparison and Usage: Compare the usage of these tools with traditional Fibonacci retracement and how they can provide a different perspective on potential price movements.
The Combination of Fibonacci Retracement with Other Technical Indicators for Increased Accuracy
Moving Averages: When a Fibonacci retracement level aligns with a key moving average, it can provide a stronger indication of potential support or resistance.
Relative Strength Index (RSI): This tool measures the speed and change of price movements. When used in conjunction with Fibonacci retracement levels, traders can find more precise buy and sell signals.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): This trend-following momentum indicator can be useful in confirming signals provided by Fibonacci retracements.
Candlestick Patterns: Fibonacci retracements can become more accurate when combined with candlestick patterns. If a certain candlestick pattern forms around a Fibonacci level, it can confirm potential price reversals.
Trend Lines and Channels: If a Fibonacci level lines up with a trend line or within a price channel, it can strengthen the level's validity.
In all cases, it's important to understand that while these advanced techniques can provide more nuanced insights, they are still just tools. No method can predict market movements with 100% accuracy, and all trading strategies should consider the trader's individual risk tolerance and investment objectives.
Common Mistakes when Using Fibonacci Retracement Levels
Identifying Common Pitfalls Traders Encounter When Using Fibonacci Retracement
Choosing Incorrect Highs and Lows: One common mistake is incorrectly identifying the most significant high and low points in a trend to draw the Fibonacci retracement levels. Choosing minor highs and lows can lead to inaccurate levels and potential misinterpretation of the price action.
Relying Solely on Fibonacci Levels: Some traders overly rely on Fibonacci levels without considering other technical indicators or market factors. Remember that Fibonacci retracement levels are just one tool in the toolkit and should be used in conjunction with other technical analysis methods.
Ignoring the Overall Trend: Traders often ignore the overall trend of the market, which can result in faulty analysis. The underlying trend of the market can significantly influence the effectiveness of Fibonacci retracement levels.
Expecting Exact Levels: It's important to understand that Fibonacci retracement levels aren't always exact. Prices often fluctuate around these levels rather than bouncing off them exactly. Treating Fibonacci levels as exact can lead to early or late entry and exit points.
Offering Strategies to Avoid These Common Mistakes
Accurate Identification of Highs and Lows: Improve your ability to identify significant highs and lows. Look for points on the chart where the price action clearly changes direction.
Use Multiple Technical Indicators: Always use Fibonacci retracement levels in conjunction with other technical analysis tools like moving averages, RSI, MACD, and candlestick patterns to confirm trading signals.
Consider the Overall Trend: Always keep the overall trend in mind when using Fibonacci retracements. They tend to be more reliable when used in the direction of the overall trend.
Treat Levels as Zones: Instead of treating Fibonacci levels as exact numbers, consider them as zones of potential support or resistance. This approach can help you manage expectations and make more informed trading decisions.
Continual Learning and Practice: Improve your skills by constantly learning and practicing. Use a demo account to practice drawing Fibonacci levels and making trades based on them. This can help you understand how they work in real-time without risking real money.
Risk Management: Always have a risk management strategy in place. This includes setting stop-loss and take-profit points, and not investing more than you can afford to lose. Remember that no indicator is perfect and trading involves risk.
Conclusion
In this article, we delved into the fascinating world of Fibonacci retracement levels and their application in trading, particularly in Forex. Originating from the unique properties of the Fibonacci sequence, these levels have found widespread use in predicting potential support and resistance zones in market trends.
We began with an exploration of the history of the Fibonacci sequence and its mathematical properties, leading us to understand its broad applications in various fields, including trading. We then proceeded to define Fibonacci retracement in the context of trading, explaining its workings and importance in Forex markets.
Through detailed analysis, we highlighted the key Fibonacci retracement levels: 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 100%. We explained their significance in trading, substantiated with graphical illustrations and practical examples. We further provided a step-by-step guide on how to use these levels in trading, focusing on their application in identifying entry and exit points and managing trading risks.
To provide a more holistic view, we also discussed advanced techniques, such as Fibonacci extensions, Fibonacci fan, and Fibonacci arc. We touched upon the potential benefits of combining Fibonacci retracement with other technical indicators to improve trading accuracy.
Finally, we highlighted some common mistakes traders make while using Fibonacci retracement levels and provided strategies to avoid them.
As powerful as Fibonacci retracement levels can be, it's important to remember that they are not foolproof. They should be used as part of a comprehensive trading strategy, and not relied upon exclusively. As with all trading tools, the key to successful trading lies in understanding, learning, practicing, and managing risk effectively. Fibonacci retracement is a valuable tool in your trading toolkit, but it works best when combined with a solid understanding of the market and a disciplined trading strategy.